Project title: Development of Large-Scale Modelling of Wildfire Propagation
Supervisors: Dr Salvador Navarro-Martinez, Dr Andrea Giusti
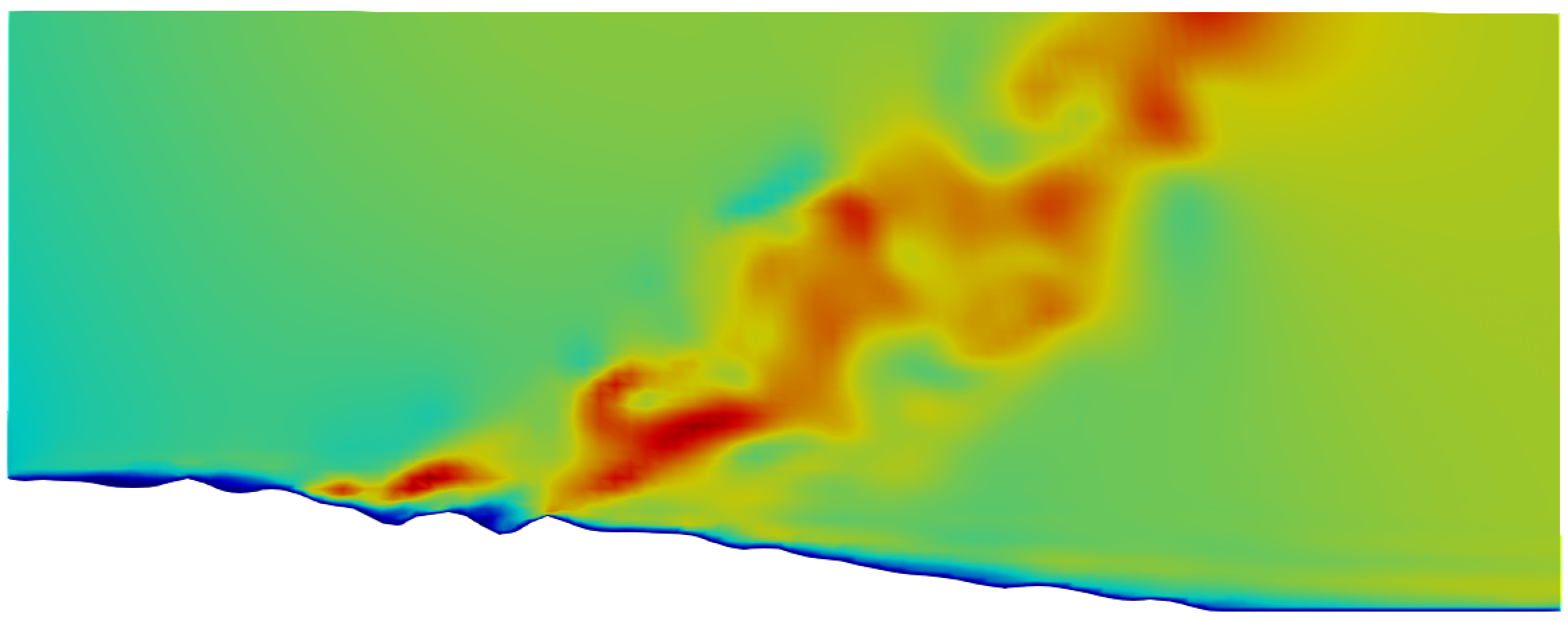
The coupled relationship between wildfires and climate change has gained rising attention due to the increase in global wildfire occurrence. Hence, effective wildfire prediction and suppression are beneficial to the environment and human population. Given the capricious behaviour of wildfires, the accurate prediction for the control of fire propagation requires a profound understanding of the factors contributing to the fire spread process. However, since large-scale experiments would not be possible in this area of study, numerical analysis by computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is required for research and operational prediction purposes.
This project has developed a model with OpenFOAM, an open-source 3D CFD software, to simulate a large-scale wildfire over complex terrains. The compound effects of the topology of terrain, vegetation types and most importantly the transient atmospheric and weather conditions have been integrated into the modelling process. Large eddy scale (LES) simulations have been employed to model the numerous length scales seen in the turbulence of wind and wildfires. As a validation of results from the numerical model, data obtained from a wildfire in Mati, Greece in 2018 was compared quantitatively and qualitatively with the results obtained.